Mold
Molds are organisms that are found indoors and outdoors. They are part of the natural environment and play an important role in our ecological system by breaking down and digesting organic material. Molds are neither plants nor animals. They are part of the kingdom Fungi.
Yeast, mold, mildew and mushrooms are common forms of fungi. Mold is essentially a description of fungi that grows on surfaces, such as the black substance on a moldy shower wall. Mold and mildew often refer to the same type of fungi. All mold is fungi, but not all fungi is mold.
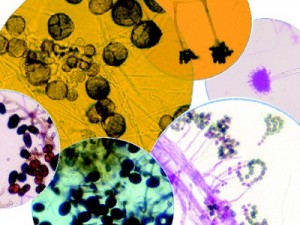
No one knows how many species of fungi exist, but estimates range from the tens of thousands to perhaps 300,000 or more. Some of the more common indoor molds are Penicillium, Aspergillus, Cladosporium and Alternaria.
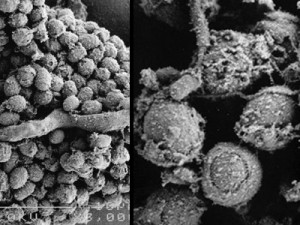
Mold may appear as a fuzzy, thread-like, cobwebby fungus, although it can never be identified with certainty without being lab-tested. Health problems caused by mold are related to high concentrations of spores in indoor air.
Molds grow in many colors, including white. “Black mold” is not a species or specific kind of mold, and neither is “toxic mold.” Sometimes, the news media use the terms “toxic mold” and “black mold” to refer to molds that may produce mycotoxins, or for a specific mold known as Stachybotrys chartarum. Molds that produce mycotoxins are often referred to as toxigenic fungi.
Molds are organisms that are found indoors and outdoors. They are part of the natural environment and play an important role in our ecological system by breaking down and digesting organic material. Molds are neither plants nor animals. They are part of the kingdom Fungi.
Yeast, mold, mildew and mushrooms are common forms of fungi. Mold is essentially a description of fungi that grows on surfaces, such as the black substance on a moldy shower wall. Mold and mildew often refer to the same type of fungi. All mold is fungi, but not all fungi is mold.
No one knows how many species of fungi exist, but estimates range from the tens of thousands to perhaps 300,000 or more. Some of the more common indoor molds are Penicillium, Aspergillus, Cladosporium and Alternaria.
Mold may appear as a fuzzy, thread-like, cobwebby fungus, although it can never be identified with certainty without being lab-tested. Health problems caused by mold are related to high concentrations of spores in indoor air.
Molds grow in many colors, including white. “Black mold” is not a species or specific kind of mold, and neither is “toxic mold.” Sometimes, the news media use the terms “toxic mold” and “black mold” to refer to molds that may produce mycotoxins, or for a specific mold known as Stachybotrys chartarum. Molds that produce mycotoxins are often referred to as toxigenic fungi.
Mold spores are like microscopic seeds (2 to 100 microns in diameter) released by mold fungi when they reproduce. Many spores are so small, they easily float through the air and can be carried for great distances by even the gentlest breeze. The number of mold spores suspended in indoor and outdoor air fluctuates from season to season, day to day, and even hour to hour.
Mold spores are ubiquitous; they are found both indoors and outdoors. Mold spores cannot be eliminated from indoor environments. Some mold spores will be found floating through the air and on settled dust; however, they will not grow if moisture is not present.
Mold spores are ubiquitous; they are found both indoors and outdoors. Mold spores cannot be eliminated from indoor environments. Some mold spores will be found floating through the air and on settled dust; however, they will not grow if moisture is not present.
Mold is impossible to identify visually and must be tested by a lab in order to be confidently labeled. A general home inspection is an inspection for safety and system defects, not a mold inspection.
Every home has mold. Moisture levels of about 20% in materials will cause mold colonies to grow. Inhaling mold spores can cause health problems in those with asthma or allergies, and can cause serious or fatal fungal infections in those with lung disease or compromised immune systems.
Mold is not usually a problem indoors—unless mold spores land on a wet or damp spot and begin growing. As molds grow, they digest whatever they are growing on. Unchecked mold growth can damage buildings and furnishings; molds can rot wood, damage drywall, and eventually cause structural damage to buildings. Mold can cause cosmetic damage, such as stains, to furnishings. The potential human health effects of mold are also a concern. It is important, therefore, to prevent mold from growing indoors.
Decay, which is rot, is also caused by fungi. Early decay cannot be seen. By the time decay becomes visible, wood may have lost up to half of its strength.
In order to grow, mold fungi require that the following conditions are present:
Oxygen;
Temperatures between approximately 45° F and 85° F;
Food. This includes a wider variety of materials found in homes; and
Moisture.
If insufficient levels of any of these requirements exist, all mold growth will stop and fungi will go dormant. Most are difficult to actually kill.
Mold can grow on virtually any organic substance. Buildings are full of organic materials that mold can use as food, including paper, cloth, wood, plant material, and even soil. Molds secrete digestive enzymes that decompose the substrate, making nutrients available. Some molds can even digest synthetic materials such as adhesives, pastes and paints.
Molds can also grow on inorganic material, such as concrete, glass and metal, because it can grow on the dirt or dust that is present on the surface of those materials.
Mold is not usually a problem indoors—unless mold spores land on a wet or damp spot and begin growing. As molds grow, they digest whatever they are growing on. Unchecked mold growth can damage buildings and furnishings; molds can rot wood, damage drywall, and eventually cause structural damage to buildings. Mold can cause cosmetic damage, such as stains, to furnishings. The potential human health effects of mold are also a concern. It is important, therefore, to prevent mold from growing indoors.
Decay, which is rot, is also caused by fungi. Early decay cannot be seen. By the time decay becomes visible, wood may have lost up to half of its strength.
In order to grow, mold fungi require that the following conditions are present:
Oxygen;
Temperatures between approximately 45° F and 85° F;
Food. This includes a wider variety of materials found in homes; and
Moisture.
If insufficient levels of any of these requirements exist, all mold growth will stop and fungi will go dormant. Most are difficult to actually kill.
Mold can grow on virtually any organic substance. Buildings are full of organic materials that mold can use as food, including paper, cloth, wood, plant material, and even soil. Molds secrete digestive enzymes that decompose the substrate, making nutrients available. Some molds can even digest synthetic materials such as adhesives, pastes and paints.
Molds can also grow on inorganic material, such as concrete, glass and metal, because it can grow on the dirt or dust that is present on the surface of those materials.
Even though mold growth may take place in the attic, mold spores can be sucked into the living areas of a residence by low air pressure. Low air pressure is usually created by the expulsion of household air from exhaust fans in bathrooms, dryers, kitchens and heating equipment.